As infrastructure development expands into challenging terrains and environmental factors increase the risk of slope instability, cable anchors have become a cornerstone of modern slope stabilization techniques. Cable anchors provide reliable solutions for securing slopes, retaining walls, and other earth structures by resisting shear forces and enhancing overall stability. This article explores the role of cable anchors, their applications, and how advancements in technology are making them a critical tool for ensuring safety and resilience in infrastructure projects.
What are Cable Anchors?
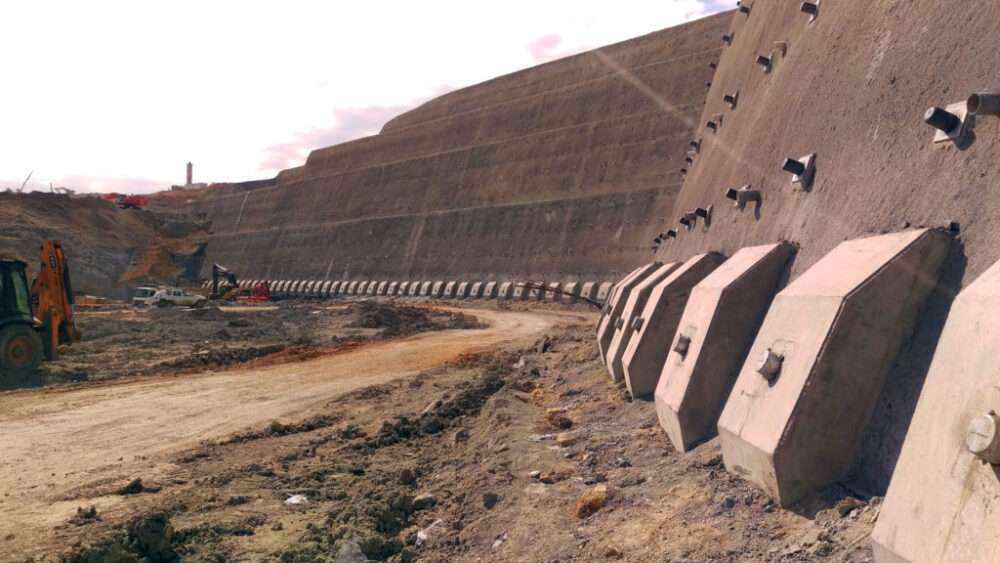
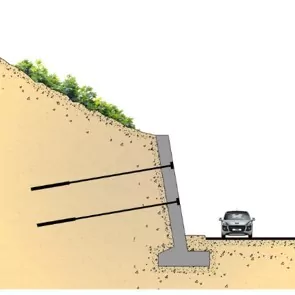
Cable anchors, also referred to as ground anchors or rock anchors, are tensioned steel cables or bars installed into soil or rock to stabilize slopes, walls, and excavations. These systems transfer tensile forces from unstable or weak layers of soil and rock to deeper, more stable strata.
A typical cable anchor system includes:
1.Anchor Head: Transfers the tension force to the slope or retaining structure.
2.Tendon (Cable or Bar): Transmits the load into the ground.
3.Grout Bond Zone: Provides anchorage by bonding the tendon to surrounding rock or soil.
Applications of Cable Anchors in Slope Stabilization
Cable anchors are versatile and widely applied in a range of slope stabilization projects, including:
1. Stabilizing Steep Slopes and Embankments
In areas where slopes are too steep or unstable for traditional methods, cable anchors provide deep reinforcement, anchoring unstable material to a stronger layer of soil or rock below. They prevent landslides, soil slippage, and other failures that compromise slope stability.
2. Retaining Wall Reinforcement
Cable anchors are commonly used to reinforce retaining walls or earth retaining structures. By applying tensile forces, they help resist lateral earth pressures and prevent wall overturning or deformation.
3. Excavation Support
During construction projects in urban areas or near critical infrastructure, cable anchors are used in combination with soil nailing or shotcrete to support excavations. They provide structural stability while allowing construction to proceed safely.
4. Landslide Mitigation
Cable anchors are essential for areas prone to landslides caused by seismic activity, heavy rainfall, or erosion. By anchoring unstable soil layers to bedrock, they reduce the risk of catastrophic slope failures.
How Cable Anchors Work
Cable anchors function by transferring tensile forces from unstable areas to more stable ground. The installation process typically involves the following steps:
1.Drilling Boreholes: Holes are drilled into the slope or retaining structure to the required depth.
2.Inserting Tendons: High-strength steel cables or bars are inserted into the boreholes.
3.Grouting the Anchor Zone: Cementitious grout is pumped into the hole to bond the cable to surrounding rock or soil.
4.Tensioning the Anchors: The cable is tensioned to apply the required load and secured with an anchor head or bearing plate.
This process ensures that tensile forces are distributed efficiently, counteracting the destabilizing forces acting on the slope or structure.
Advantages of Cable Anchors in Slope Stabilization
1. High Load-Bearing Capacity
Cable anchors provide exceptional strength and can bear significant tensile loads, making them suitable for stabilizing large or steep slopes where other methods may fail.
2. Flexibility and Adaptability
Cable anchors can be installed at various depths and angles, allowing engineers to customize their design based on site-specific conditions and stability requirements.
3. Minimal Environmental Disruption
Compared to massive retaining structures or earthworks, cable anchors cause minimal disruption to the surrounding environment, preserving existing landscapes.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
While providing robust stability, cable anchor systems are often more cost-effective than traditional slope stabilization methods like large retaining walls or soil replacement.
5. Long-Term Stability
Anchors offer long-term reliability and performance, making them ideal for critical infrastructure projects, such as highways, railways, and dams.
Innovations in Cable Anchor Technology
Advancements in materials and installation techniques have significantly improved the efficiency and reliability of cable anchors. Key innovations include:
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials: The use of epoxy-coated, stainless steel, or galvanized cables ensures durability in corrosive environments.
- Post-Tensioning Systems: Post-tensioned anchors allow engineers to apply precise loads, improving performance and adaptability.
- Self-Drilling Anchors: These anchors simplify the installation process, particularly in weak or unstable soils, by combining drilling and grouting into a single step.
- Monitoring Systems: Advanced sensors and load-monitoring devices allow real-time assessment of anchor performance, ensuring ongoing safety and stability.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
1. Highway Slope Stabilization
In mountainous regions prone to landslides, cable anchors have been successfully used to stabilize steep highway embankments, ensuring safe road conditions and uninterrupted transportation.
2. Urban Excavation Projects
In cities with limited space for construction, cable anchors are used to reinforce deep excavations, preventing collapse while enabling the construction of underground parking, metro tunnels, and basements.
3. Dam Stability
For dams built on weak foundations, cable anchors provide reinforcement to prevent movement and structural failure, ensuring the safety and functionality of the dam.
Conclusion
Cable anchors play a pivotal role in modern slope stabilization, offering a reliable and versatile solution for addressing instability challenges. Their ability to resist tensile forces, provide deep reinforcement, and adapt to a variety of conditions makes them indispensable in infrastructure, construction, and landslide mitigation projects. With ongoing advancements in materials and monitoring technologies, cable anchors will continue to evolve, providing stronger, safer, and more sustainable solutions for slope stabilization in an ever-changing environment.
Keywords: cable anchors, slope stabilization, ground anchors, retaining wall reinforcement, post-tensioned anchors, landslide mitigation, soil stabilization