Tam grouting, also referred to as Tube-a-Manchette grouting, is a specialized ground improvement technique designed to enhance the stability and integrity of soil in construction projects. This precise and controlled method is commonly employed to address weak soils, fill voids, and reduce permeability, making it a vital tool in geotechnical engineering.
What is Tam Grouting?
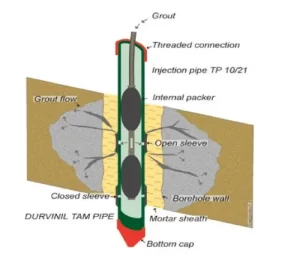
Tam grouting involves the injection of grout through pre-installed sleeve pipes, or manchettes, that are placed within boreholes. These pipes have small openings covered by rubber sleeves, which act as one-way valves, allowing grout to be selectively injected into targeted zones under pressure.
This method is distinct due to its precision, enabling engineers to stabilize specific weak areas without disrupting the surrounding soil structure.
Key Components of Tam Grouting
1.Tube-a-Manchette (Sleeve Pipe):
-
- A flexible, perforated pipe with valves designed to allow grout injection while preventing backflow.
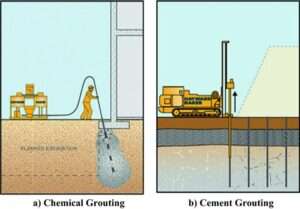
2.Grout Materials:
-
- Cement-based slurries for strength improvement.
- Chemical grouts like silicates or polyurethane for permeability reduction.
3.Grout Pumping System:
-
- High-pressure pumps that control the flow and injection rate of grout.
4.Monitoring Systems:
-
- Real-time sensors to measure pressure and flow, ensuring optimal application.
The Tam Grouting Process
1. Borehole Drilling
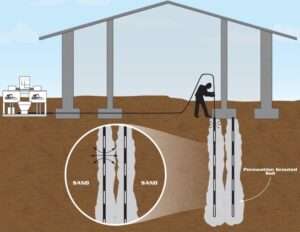
Boreholes are drilled to the desired depth at targeted locations. These serve as pathways for the insertion of the sleeve pipes.
2. Installation of Sleeve Pipes
Tube-a-Manchette pipes are inserted into the boreholes and sealed with a temporary casing or backfill material to prevent grout from escaping to unintended areas.
3. Grout Injection
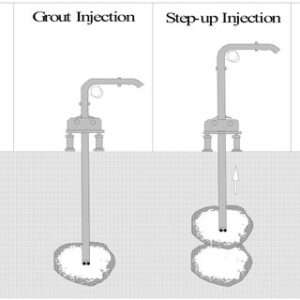
Grout is pumped at controlled pressures through specific sections of the sleeve pipe, where it exits via the valves and penetrates the surrounding soil.
- Stage Grouting: Grout is injected in stages to ensure uniform treatment.
- Repeat Grouting: Additional grout may be injected later for further stabilization.
Applications of Tam Grouting
Tam grouting is employed in a variety of scenarios, including:
- Foundation Strengthening: Reinforcing soil under buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Seepage Control: Reducing water ingress in tunnels, dams, and retaining walls.
- Void Filling: Filling gaps in soil caused by sinkholes or subsurface erosion.
- Underpinning Structures: Stabilizing existing buildings during renovation or excavation.
Advantages of Tam Grouting
- Precision: Enables targeted soil improvement in localized areas.
- Flexibility: Adaptable to various soil conditions and project requirements.
- Minimized Disruption: Does not disturb the natural stratification of soil.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces risks associated with soil instability.
Challenges and Considerations
While Tam grouting is highly effective, it requires careful planning and execution:
- Cost: High precision and equipment can increase overall costs.
- Soil Compatibility: Effectiveness depends on soil permeability and grout type.
- Environmental Impact: Proper containment of grout is necessary to avoid contamination.
Future Trends in Tam Grouting
Advancements in materials and monitoring technology are improving the efficiency of Tam grouting. Innovations such as smart sensors and AI-based modeling allow for more precise control, reducing material waste and environmental impact.
Conclusion
Tam grouting is a cornerstone technique in modern geotechnical engineering, offering unparalleled control and effectiveness in ground stabilization. Its ability to target specific zones, coupled with its adaptability to diverse soil conditions, makes it an invaluable tool in ensuring the safety and durability of construction projects. With ongoing technological advancements, the potential of Tam grouting continues to expand, paving the way for even more robust and sustainable ground improvement solutions.