Self-drilling anchors (SDAs) represent a groundbreaking advancement in geotechnical engineering, offering a highly efficient solution for slope stabilization and ground support. These anchors combine drilling and anchoring into a single operation, significantly streamlining installation processes. This article explores the features, benefits, and applications of self-drilling anchors, emphasizing their impact on modern construction.
What Are Self-Drilling Anchors?
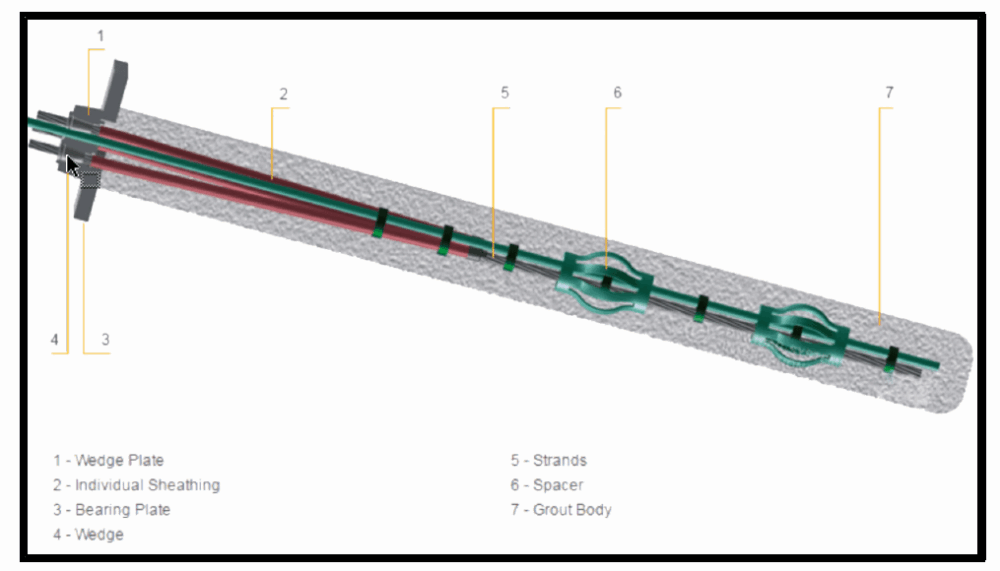
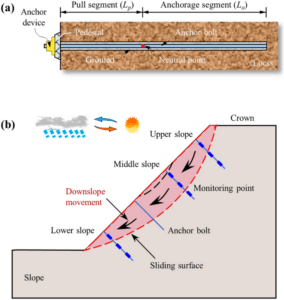
Self-drilling anchors are specialized systems designed to stabilize unstable ground or support structures in challenging conditions. They consist of a hollow steel rod with a sacrificial drill bit at the tip, which allows simultaneous drilling and grouting. The hollow rod serves as both the drill string and the anchor tendon, simplifying the installation process.
How Do Self-Drilling Anchors Work?
The installation of SDAs involves a seamless process that integrates drilling and anchoring. Key steps include:
1.Drilling: The sacrificial drill bit penetrates the ground while the hollow rod advances into the substrate.
2.Grouting: Grout is pumped through the hollow rod to fill the borehole and secure the anchor in place.
3.Tensioning (Optional): For certain applications, the anchor is tensioned to provide additional support.
This efficient process reduces installation time and minimizes the need for additional equipment or steps.
Applications of Self-Drilling Anchors
Self-drilling anchors are widely used in various geotechnical and structural projects, including:
1.Slope Stabilization: Preventing landslides and erosion on steep slopes.
2.Excavation Support: Reinforcing retaining walls and cut slopes during construction.
3.Tunneling: Providing ground support in weak or fractured rock conditions.
4.Foundations: Enhancing stability for structures in soft or unstable soils.
5.Mining: Securing underground mine walls and ceilings.
Advantages of Self-Drilling Anchors
1.Time Efficiency: Combines drilling and anchoring into one operation, reducing project timelines.
2.Adaptability: Suitable for a variety of ground conditions, including loose soil and fractured rock.
3.Cost-Effectiveness: Minimizes labor and equipment requirements.
4.High Load Capacity: Provides reliable support in demanding applications.
5.Simplified Installation: Eliminates the need for pre-drilling and casing in many situations.
Challenges and Considerations
While self-drilling anchors offer significant advantages, some challenges must be addressed:
- Corrosion Protection: Proper measures are necessary to ensure long-term durability.
- Specialized Equipment: Requires specific tools and expertise for installation.
- Material Selection: The choice of drill bit and rod must align with ground conditions.
Conclusion
Self-drilling anchors are an innovative technology revolutionizing slope stabilization and ground support. Their ability to streamline installation and adapt to challenging conditions makes them an indispensable tool in geotechnical engineering. As advancements in materials and techniques continue, self-drilling anchors will play a pivotal role in shaping resilient and efficient infrastructure projects worldwide.