Introduction
Deep excavations present significant engineering challenges, particularly in urban areas where space constraints and soil conditions necessitate innovative solutions. Secant pile walls offer a robust approach to providing both structural support and effective groundwater control, making them a preferred choice for deep excavation projects.
What Are Secant Pile Walls?
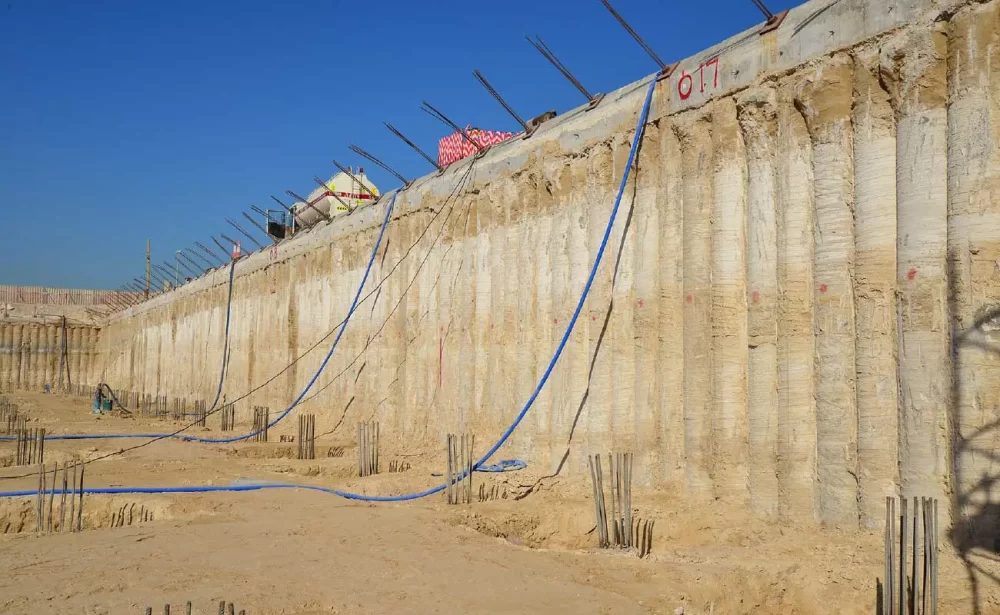
Secant pile walls consist of a series of overlapping drilled shafts, known as piles, that form a continuous barrier in the ground. These piles are typically constructed using a sequence of primary (soft) and secondary (hard) piles, with the latter reinforced with steel or concrete to provide additional strength. The interlocking nature of secant pile walls enhances their ability to resist lateral earth pressures and prevent water infiltration.
Key Benefits of Secant Pile Walls
1.Enhanced Structural Integrity: By interlocking piles, secant pile walls create a continuous structure capable of withstanding high lateral loads, making them suitable for deep excavations near existing structures.
2.Effective Waterproofing: The overlapping piles significantly reduce water seepage, minimizing the need for additional dewatering systems and ensuring a dry excavation site.
3.Versatility in Soil Conditions: These walls are adaptable to a variety of soil types, including granular and cohesive soils, making them applicable across different geological settings.
4.Space Efficiency: Unlike other retention systems, secant pile walls require minimal workspace, making them ideal for urban construction projects where site constraints are a concern.
5.Reduced Environmental Impact: Since secant pile walls minimize ground movement and vibration, they reduce the risk of damage to nearby structures and utilities, which is critical in densely populated areas.
Construction Process
The construction of secant pile walls follows a systematic approach:
1.Site Preparation: Engineers assess the soil conditions and groundwater levels to determine the optimal pile configuration.
2.Drilling and Pile Installation: Primary piles are first installed using a soft mix of concrete or bentonite-cement slurry. Once set, secondary piles, reinforced with steel cages or higher-strength concrete, are drilled and poured in between the primary piles.
3.Curing and Reinforcement: The wall is allowed to cure, ensuring structural integrity and water tightness before excavation proceeds.
4.Excavation and Anchoring (if required): As excavation advances, additional reinforcements such as anchors or struts may be introduced to enhance stability.
Applications of Secant Pile Walls
Secant pile walls are commonly used in:
- Basement Construction: Providing structural support and groundwater control for deep foundations.
- Tunnels and Underground Infrastructure: Ensuring stability and waterproofing in metro and sewer construction.
- Slope Stabilization: Preventing landslides and erosion in unstable terrains.
- Flood Defense Systems: Serving as barriers to protect against rising water levels in flood-prone areas.
Conclusion
Secant pile walls are an essential technology in modern deep excavation projects, combining strength, waterproofing, and versatility to address complex engineering challenges. Their ability to provide structural support while minimizing environmental impact makes them a preferred choice for urban and infrastructure developments. With advancements in construction techniques and materials, secant pile walls will continue to play a crucial role in sustainable excavation solutions.