Introduction
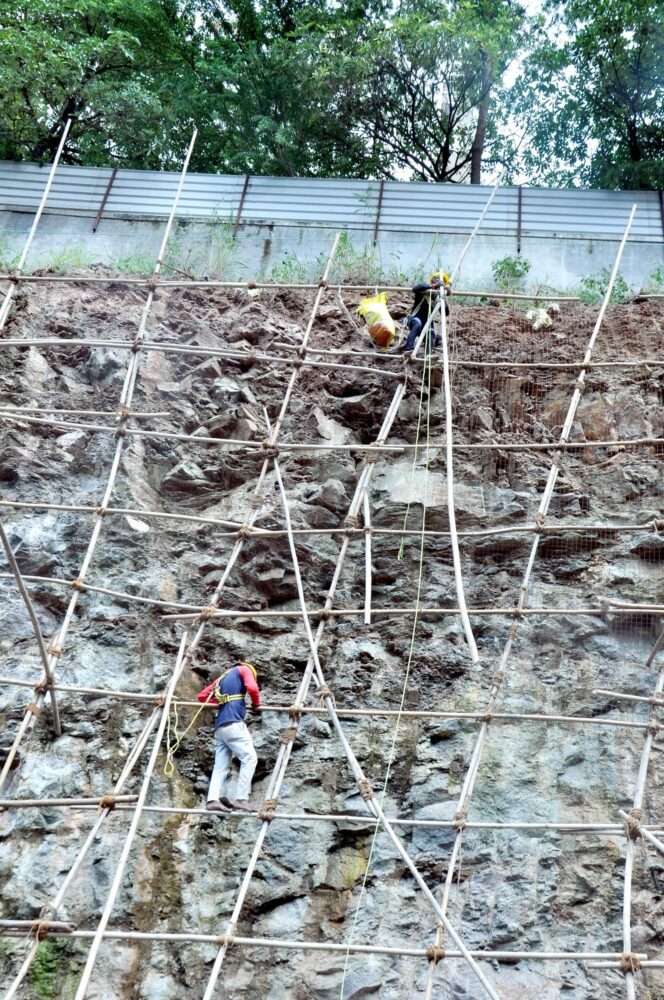
Rockfall barriers are crucial engineering solutions designed to mitigate the risks associated with falling rocks and debris in mountainous regions, construction sites, and transportation corridors. These barriers effectively absorb and dissipate impact energy, preventing damage to infrastructure and ensuring public safety. This article explores the types, advantages, and applications of rockfall barriers in hazard mitigation.
Types of Rockfall Barriers
1.Flexible Rockfall Barriers – Constructed from high-tensile steel wire mesh, these barriers are designed to absorb high-impact forces while remaining adaptable to terrain variations.
2.Rigid Rockfall Barriers – Made from reinforced concrete or steel, these barriers provide a strong, immovable defense against falling debris.
3.Catchment Fences – Installed at the base of slopes, these fences collect falling rocks and prevent them from reaching critical areas.
4.Attenuation Systems – These systems slow down falling rocks by guiding them into controlled collection areas, reducing impact forces.
5.Hybrid Systems – A combination of flexible and rigid barriers, offering enhanced protection in high-risk areas.
Advantages of Rockfall Barriers
- High Energy Absorption: Designed to withstand significant impact forces from rockfalls.
- Customizable Solutions: Can be tailored to different slope conditions and rockfall intensities.
- Minimal Environmental Impact: Does not require extensive land modifications.
- Quick and Efficient Installation: Can be deployed rapidly with minimal site disturbance.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: Prevents damage to infrastructure, reducing maintenance and repair costs.
Applications of Rockfall Barriers
1.Road and Highway Protection – Prevents rockfalls from reaching vehicles and pedestrians.
2.Railway Safety – Shields rail tracks from rockfall-related obstructions and accidents.
3.Construction and Excavation Sites – Enhances worker safety in areas prone to slope instability.
4.Mining and Quarry Operations – Secures excavation sites and protects equipment from falling debris.
5.Hydropower and Dam Infrastructure – Ensures the safety of critical energy and water supply facilities.
Conclusion
Rockfall barriers are an essential component of hazard mitigation strategies, offering effective protection against falling rocks in high-risk areas. With advanced designs and materials, these barriers continue to evolve, providing enhanced safety and durability in geotechnical and infrastructure projects. As the demand for resilient infrastructure grows, rockfall barriers will remain a vital tool in ensuring slope stability and public safety.