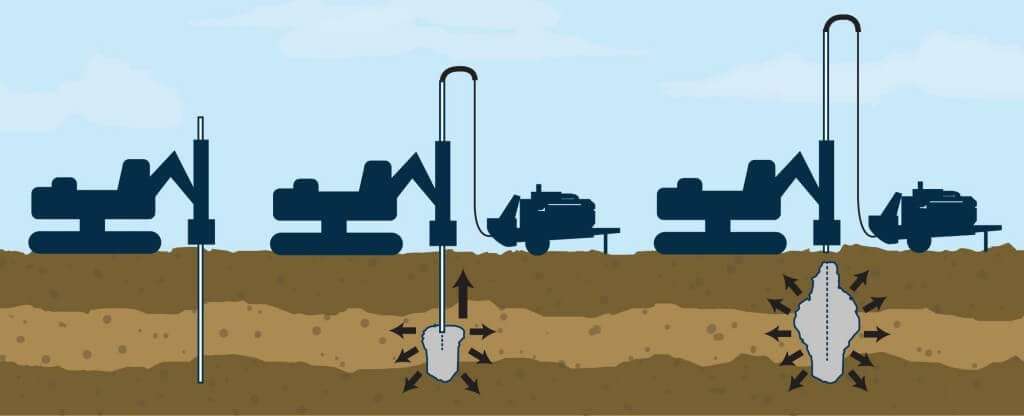
Permeation grouting is a widely used technique for ground stabilization and waterproofing in civil engineering and construction projects. It involves injecting a low-viscosity grout into porous soil or rock formations to improve their strength, reduce permeability, and mitigate water ingress. This method is particularly effective in enhancing foundation stability, reinforcing tunnel linings, and preventing water seepage in underground structures.
Principles of Permeation Grouting
The process of permeation grouting relies on the ability of the grout material to permeate voids and fractures within the soil or rock mass without significantly disturbing the existing structure. The injected grout hardens over time, creating a solidified matrix that enhances load-bearing capacity and reduces water flow through the treated area.
Materials Used in Permeation Grouting
Common grout materials used in permeation grouting include:
- Cementitious Grouts: Typically used for coarse-grained soils where permeability allows grout penetration.
- Silicate-Based Grouts: Suitable for fine-grained soils due to their low viscosity and controlled gel times.
- Polyurethane and Epoxy Resins: Effective for sealing water leaks and reinforcing fragile geological formations.
Applications of Permeation Grouting
Permeation grouting is widely applied in various construction and infrastructure projects, such as:
- Foundation Stabilization: Strengthening weak soils beneath buildings, bridges, and roadways.
- Underground Structures: Preventing water ingress in tunnels, basements, and metro systems.
- Dam and Levee Rehabilitation: Enhancing the impermeability of water-retaining structures.
- Excavation Support: Reducing risks of collapse and improving soil cohesion around deep excavations.
Advantages of Permeation Grouting
- Improved Soil Strength: Enhances the load-bearing properties of the treated ground.
- Effective Waterproofing: Reduces permeability and prevents water intrusion in critical structures.
- Minimal Disruption: Can be applied without significant excavation or disturbance to the existing site.
- Versatility: Adaptable to different soil types and environmental conditions.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, permeation grouting requires careful planning and execution. Key challenges include:
- Selection of Appropriate Grout Material: Ensuring compatibility with soil conditions and project requirements.
- Control of Grout Flow and Distribution: Preventing excessive grout loss and ensuring uniform coverage.
- Cost Considerations: Managing material and labor costs while achieving optimal performance.
Conclusion
Permeation grouting is a proven and effective technique for ground stabilization and waterproofing in a wide range of construction projects. Its ability to improve soil strength, reduce permeability, and provide long-term durability makes it a valuable solution in geotechnical and civil engineering applications. With proper material selection and execution, permeation grouting can enhance the safety and longevity of infrastructure projects.