Ground improvement is a crucial technique in geotechnical engineering, aimed at enhancing the physical properties of soil to support the construction of safe, stable, and durable structures. Whether for buildings, bridges, roads, or other infrastructure, this practice addresses challenges posed by weak or unstable soil conditions, ensuring the longevity and reliability of projects.
The Importance of Ground Improvement
In many construction scenarios, the existing soil is incapable of supporting the intended load due to poor strength, high compressibility, or susceptibility to water retention. Without proper intervention, this can lead to structural issues such as uneven settlement, reduced load-bearing capacity, and even catastrophic failure. Ground improvement mitigates these risks by modifying the soil’s properties to meet specific engineering requirements.
Common Ground Improvement Techniques
Several methods are employed to improve soil conditions, each tailored to address specific challenges. Key techniques include:
1.Soil Stabilization
This involves adding stabilizing agents, such as lime, cement, or fly ash, to improve soil strength and reduce its plasticity. It is widely used for road construction and building foundations.
2.Dynamic Compaction
Heavy weights are repeatedly dropped onto the ground surface to compact loose soils. This method is effective for improving granular soils and reducing void spaces.
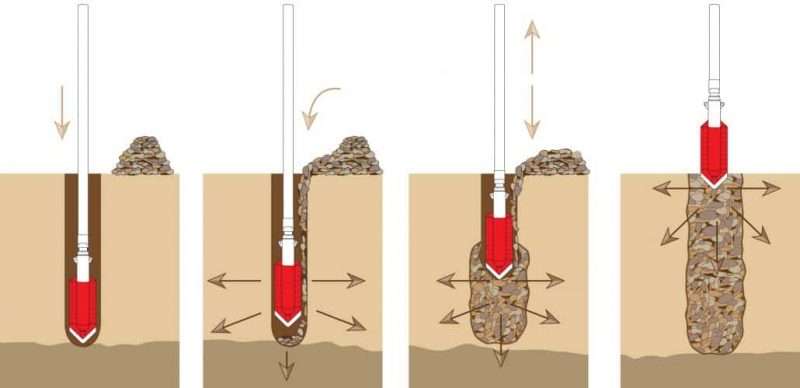
3.Vibro Techniques
Techniques like vibro-compaction and vibro-replacement use specialized equipment to compact or replace weak soil with more stable materials, such as gravel.
4.Grouting
A process where grout materials, like cement or chemical solutions, are injected into the ground to fill voids and strengthen the soil. This method is often used to seal cracks and prevent water infiltration.
5.Geosynthetics
Geotextiles, geogrids, and geomembranes are used to reinforce soil and improve its load distribution capacity. These materials are especially useful in slope stabilization and embankment construction.
Benefits of Ground Improvement
1.Increased Load-Bearing Capacity
Improved soil can handle heavier loads, allowing for the construction of larger and more complex structures.
2.Reduced Settlement
Ground improvement minimizes uneven settlement, preventing structural damage and ensuring the longevity of buildings and infrastructure.
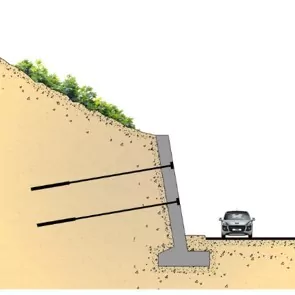
3.Enhanced Stability
Strengthened soil resists lateral forces, reducing the risk of landslides and slope failures, particularly in seismically active regions.
4.Improved Drainage and Water Resistance
Techniques like grouting and soil stabilization help manage water infiltration, reducing erosion and ensuring soil integrity.
Applications in Modern Construction
Ground improvement is vital for projects built on challenging terrain, such as soft clay, loose sand, or reclaimed land. It is extensively used in urban development, transportation infrastructure, and industrial construction. For example, techniques like jet grouting are employed to stabilize foundations for high-rise buildings in coastal cities, while dynamic compaction is applied to prepare land for airport runways.
Conclusion
By enhancing the safety and stability of soil, ground improvement not only ensures the success of construction projects but also protects lives and investments. As engineering challenges grow with urbanization and climate change, innovative ground improvement techniques will play an even more significant role in shaping resilient infrastructure for the future.