In construction, a stable foundation is critical for safety, durability, and long-term performance. Compaction grouting has emerged as a powerful geotechnical technique to enhance soil stability, particularly in challenging environments where soil integrity is compromised. This article explores the key principles, benefits, and applications of compaction grouting in modern construction projects.
What is Compaction Grouting?
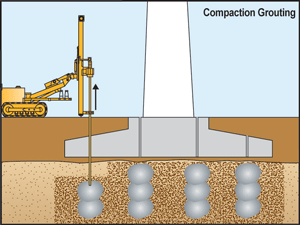
Compaction grouting is a specialized ground improvement method that involves injecting a low-mobility grout into the soil. The grout, typically a cementitious or sand-based mixture, is pumped under high pressure to displace and compact loose soil particles. Unlike permeation grouting, where the material flows into soil voids, compaction grouting forms a dense bulb of grout that consolidates the surrounding soil.
How Compaction Grouting Works
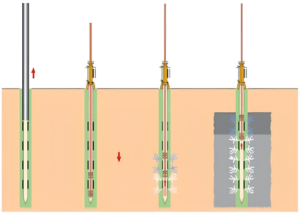
1.Preparation: A thorough site investigation is conducted to evaluate soil conditions and determine the areas requiring improvement.
2.Drilling: Small-diameter boreholes are drilled to the target depth.
3.Injection: Grout is injected incrementally from the deepest point upward, ensuring systematic soil compaction and minimizing voids.
4.Monitoring: Real-time monitoring ensures that the desired pressure and compaction levels are achieved.
Advantages of Compaction Grouting
- Improves Load-Bearing Capacity: By compacting loose soils, the technique increases the strength and stability of the foundation.
- Minimizes Settlement: It addresses uneven settlement issues, protecting structures from potential damage.
- Versatility: Effective in a range of soil types, including granular soils and loose fills.
- Precision: Advanced monitoring techniques allow for controlled application, reducing the risk of over-grouting or unnecessary disruption.
- Cost-Effective: Prevents the need for costly foundation repairs or complete soil replacement.
Applications in Construction Projects
- Foundation Stabilization: Enhances the soil’s ability to support heavy structures, such as buildings, bridges, and towers.
- Remediation of Sinkholes: Provides a reliable solution for filling voids and stabilizing ground affected by sinkholes.
- Infrastructure Repair: Used to stabilize soils under roads, railways, and airport runways experiencing subsidence.
- Earthquake-Resilient Foundations: Reduces liquefaction risks in earthquake-prone areas by densifying loose, saturated soils.
Environmental and Practical Considerations
Compaction grouting is not without its challenges. Environmental factors, such as proximity to water bodies or protected areas, require careful planning to prevent contamination. Additionally, the choice of grout material and injection pressures must align with site-specific requirements to avoid over-compaction or structural damage.
Conclusion
Compaction grouting is a transformative technique in modern construction, offering a robust solution to soil stability challenges. Its ability to enhance foundation integrity, minimize settlement, and adapt to diverse geotechnical conditions makes it an indispensable tool for engineers. By leveraging this technology, construction projects can achieve safer and more resilient outcomes, even in complex soil environments.