Introduction
Ground improvement techniques are essential for enhancing soil stability, increasing load-bearing capacity, and mitigating settlement risks in construction projects. These methods allow engineers to modify weak or problematic soils, ensuring safe and durable foundations for buildings, roads, and infrastructure.
Importance of Ground Improvement
Poor soil conditions can lead to structural failures, excessive settlement, and instability. Ground improvement techniques provide solutions by:
- Increasing Bearing Capacity: Strengthening soil to support heavy structures.
- Reducing Settlement: Minimizing uneven ground movement over time.
- Enhancing Slope Stability: Preventing landslides and erosion in hilly terrains.
- Mitigating Liquefaction Risks: Improving soil performance during seismic events.
Common Ground Improvement Techniques
Several ground improvement methods are used based on soil conditions, project requirements, and cost considerations:
1.Mechanical Stabilization
- Compaction: Increases soil density through vibratory rollers, tamping, or dynamic compaction.
- Soil Replacement: Removing weak soil and replacing it with compacted granular material.
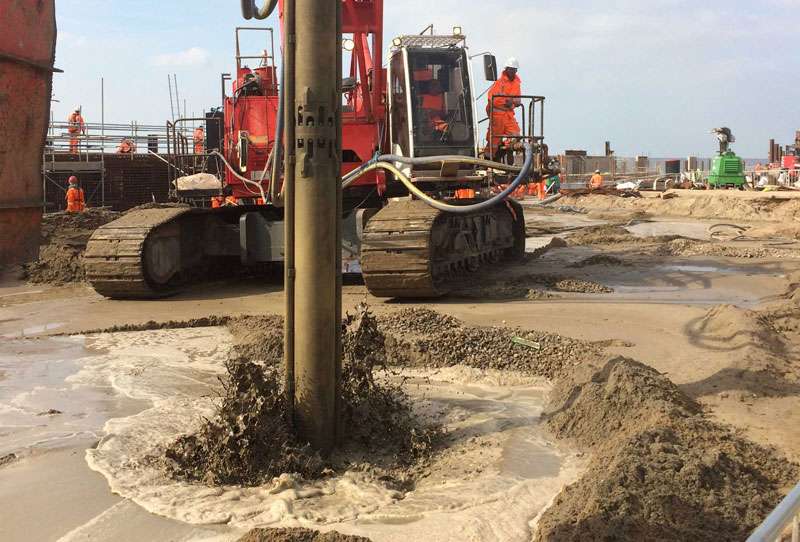
2.Grouting Techniques
- Permeation Grouting: Injecting cementitious or chemical grout to fill voids and bind soil particles.
- Jet Grouting: High-pressure grout injection creates soil-cement columns for strength enhancement.
3.Reinforcement Methods
- Soil Nailing: Installing steel bars or geosynthetic reinforcements to stabilize slopes and excavations.
- Geogrids and Geotextiles: Enhancing soil strength and load distribution in embankments and roads.
4.Soil Mixing and Chemical Stabilization
- Deep Soil Mixing (DSM): Combining soil with cement or lime to improve strength and reduce permeability.
- Chemical Stabilization: Using additives like lime, fly ash, or polymers to modify soil properties.
5.Drainage and Dewatering Techniques
- Prefabricated Vertical Drains (PVDs): Accelerating soil consolidation by expelling excess water.
- Well Point Systems: Lowering groundwater levels to improve soil strength during excavation.
6.Vibro Techniques
- Vibro Compaction: Compacting loose sands using deep vibratory probes.
- Vibro Stone Columns: Installing gravel-filled columns to reinforce soft soils and improve drainage.
Applications of Ground Improvement
Ground improvement techniques are used in various construction and infrastructure projects, including:
- Foundation Support: Strengthening soils for high-rise buildings and bridges.
- Highways and Railways: Reducing settlement risks and improving subgrade conditions.
- Ports and Marine Structures: Enhancing soil stability for offshore platforms and retaining walls.
- Slope Protection: Preventing landslides and erosion in hilly areas.
Best Practices for Ground Improvement
To ensure effective soil stabilization, engineers follow these best practices:
- Conduct geotechnical investigations to assess soil properties and choose the right technique.
- Consider cost-benefit analysis for selecting the most suitable method.
- Monitor soil behavior and settlement rates using real-time instrumentation.
- Implement quality control measures during and after construction.
Conclusion
Ground improvement techniques play a crucial role in modern construction by enhancing soil stability and ensuring the long-term performance of structures. With advancements in engineering and materials, these methods continue to evolve, offering more efficient and sustainable solutions for challenging soil conditions.