Introduction
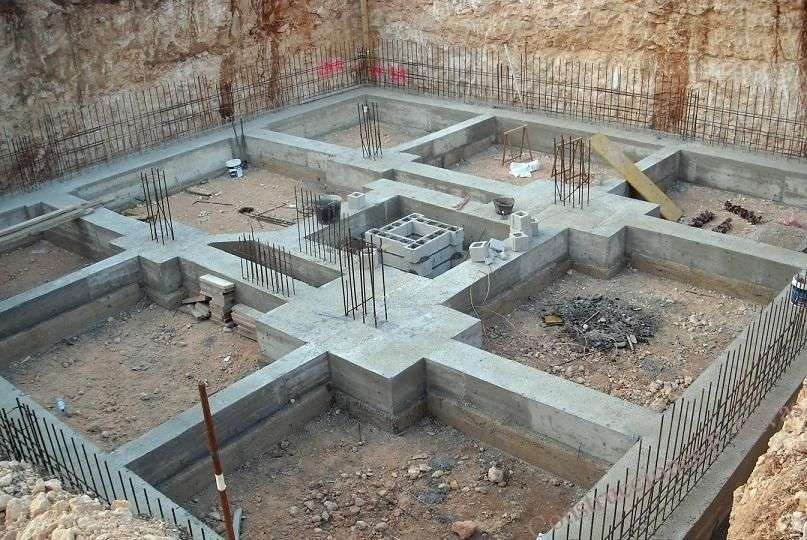
Foundation engineering is a critical aspect of civil engineering that ensures the stability and longevity of structures. It involves the analysis, design, and implementation of foundation systems that support buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure. This article explores key principles, foundation types, construction techniques, and best practices in foundation engineering.
Principles of Foundation Engineering
1.Load Distribution – Ensuring that structural loads are evenly transferred to the ground to prevent settlement or failure.
2.Soil-Structure Interaction – Understanding soil properties and their behavior under loading conditions.
3.Bearing Capacity – Determining the maximum load the soil can support without excessive settlement.
4.Settlement Control – Minimizing differential settlement to prevent structural damage.
5.Durability and Stability – Designing foundations that resist environmental effects such as erosion, water table fluctuations, and seismic activity.
Types of Foundations
1.Shallow Foundations
- Spread Footings – Support individual columns or walls by spreading loads over a wider area.
- Mat (Raft) Foundations – Distribute loads over the entire building footprint, ideal for weak soils.
- Strip Footings – Provide continuous support for walls and load-bearing structures.
2.Deep Foundations
- Piles – Long, slender elements driven into the ground to transfer loads to deeper, stable layers.
- Micropiles – Small-diameter piles used in constrained spaces or retrofitting existing foundations.
- Caissons (Drilled Shafts) – Large-diameter foundations used for heavy structures, bridges, and high-rise buildings.
Construction Techniques
1.Excavation and Site Preparation – Clearing, grading, and compacting the site for foundation placement.
2.Soil Improvement Methods – Techniques such as compaction, grouting, and soil stabilization to enhance bearing capacity.
3.Reinforcement and Concrete Pouring – Using steel reinforcements and high-quality concrete to enhance foundation strength.
4.Waterproofing and Drainage Systems – Preventing water infiltration and mitigating hydrostatic pressure on foundations.
5.Quality Control and Testing – Conducting load tests, soil analysis, and inspections to ensure foundation integrity.
Best Practices in Foundation Engineering
- Comprehensive Site Investigation – Conducting geotechnical surveys to assess soil and groundwater conditions.
- Proper Material Selection – Choosing durable materials that resist environmental stressors.
- Adherence to Design Codes – Following industry standards and regulations for safe foundation design.
- Regular Maintenance and Monitoring – Inspecting foundations periodically to detect and address potential issues early.
Conclusion
Foundation engineering is essential for creating stable and resilient structures. By applying sound engineering principles, selecting appropriate foundation types, and utilizing advanced construction techniques, engineers can ensure the safety and durability of built environments. As technology and materials evolve, the field of foundation engineering continues to advance, offering innovative solutions for complex structural challenges.