Introduction
Foundation engineering is a critical aspect of construction that ensures buildings and infrastructure remain stable, durable, and safe. A well-designed foundation distributes loads efficiently, prevents structural failures, and mitigates risks associated with soil movement and environmental factors. This article explores key techniques used in foundation engineering to achieve stability and longevity in construction projects.
1.Site Investigation and Soil Analysis
Before designing a foundation, a thorough site investigation is essential. This process includes:
- Soil Testing – Determines bearing capacity, moisture content, and soil type.
- Geotechnical Surveys – Assesses soil stability, groundwater levels, and potential settlement risks.
- Load Assessment – Ensures the foundation can support the structure’s weight and external forces like wind and seismic activity.
2.Types of Foundations
Foundations are classified into two main types based on soil conditions and load requirements:
Shallow Foundations:
- Strip Foundations – Used for load-bearing walls and lightweight structures.
- Raft Foundations – Suitable for weak soils, distributing loads across a large area.
- Pad Foundations – Ideal for individual columns in reinforced concrete structures.
Deep Foundations:
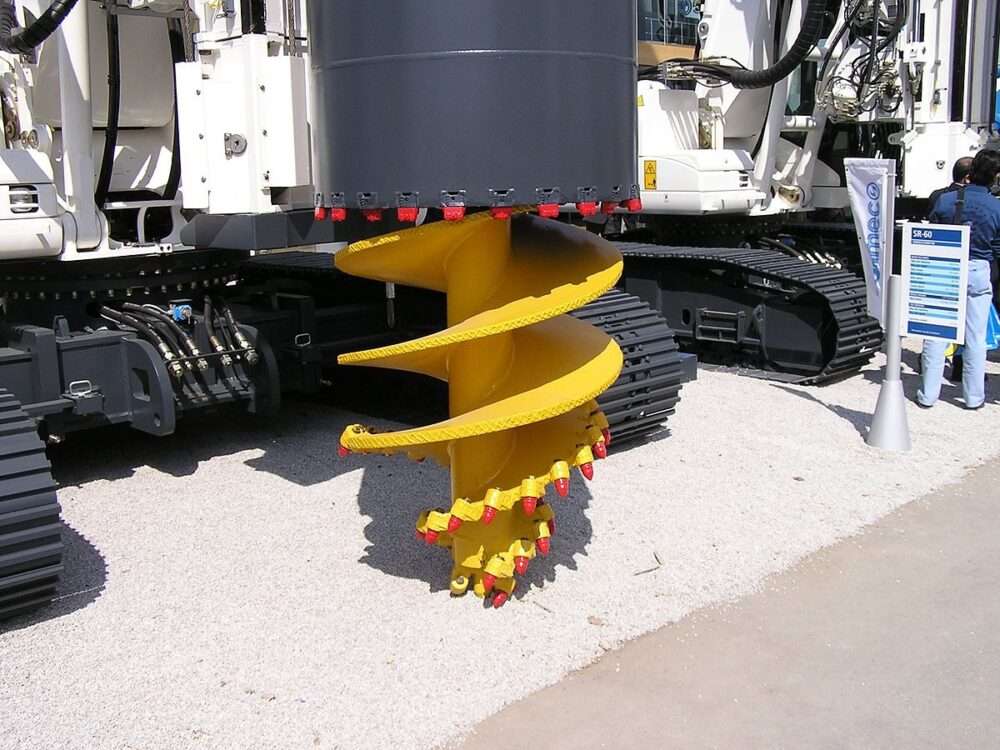
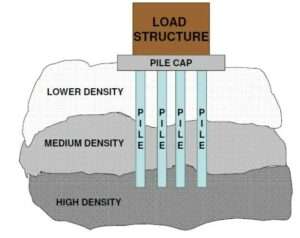
- Pile Foundations – Used in unstable soil conditions, transferring loads to deeper, more stable layers.
- Pier Foundations – Common in bridge construction, providing strong load-bearing capacity.
- Caisson Foundations – Utilized in underwater construction to support heavy structures.
3.Advanced Construction Techniques
Innovations in foundation engineering have led to more efficient and resilient construction methods:
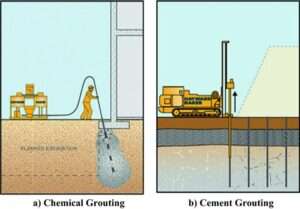
- Soil Stabilization – Techniques like grouting, chemical treatment, and compaction improve soil strength.
- Underpinning – Strengthens existing foundations to support additional loads or repair settlement issues.
- Deep Soil Mixing – Enhances weak soils by injecting cementitious materials for increased stability.
4.Addressing Environmental and Seismic Concerns
To ensure durability, foundation engineers must consider external factors such as:
- Seismic Design – Incorporating flexible foundation systems and base isolators to absorb earthquake forces.
- Flood Protection – Elevating foundations or using waterproof materials to prevent structural damage.
- Sustainable Practices – Using eco-friendly materials and techniques to minimize environmental impact.
Conclusion
Foundation engineering plays a crucial role in ensuring the longevity and stability of structures. By integrating proper site analysis, selecting suitable foundation types, and employing advanced construction techniques, engineers can create foundations that withstand environmental challenges and support resilient infrastructure.