In modern construction, deep excavations often require robust solutions for retaining earth and preventing groundwater infiltration. Contiguous pile walls are one of the most effective and commonly used systems for these purposes, providing structural support and stability in challenging conditions. These walls, made from interlocking piles, are a practical choice for projects that require deep excavation with minimal disruption to surrounding areas.
What Are Contiguous Pile Walls?
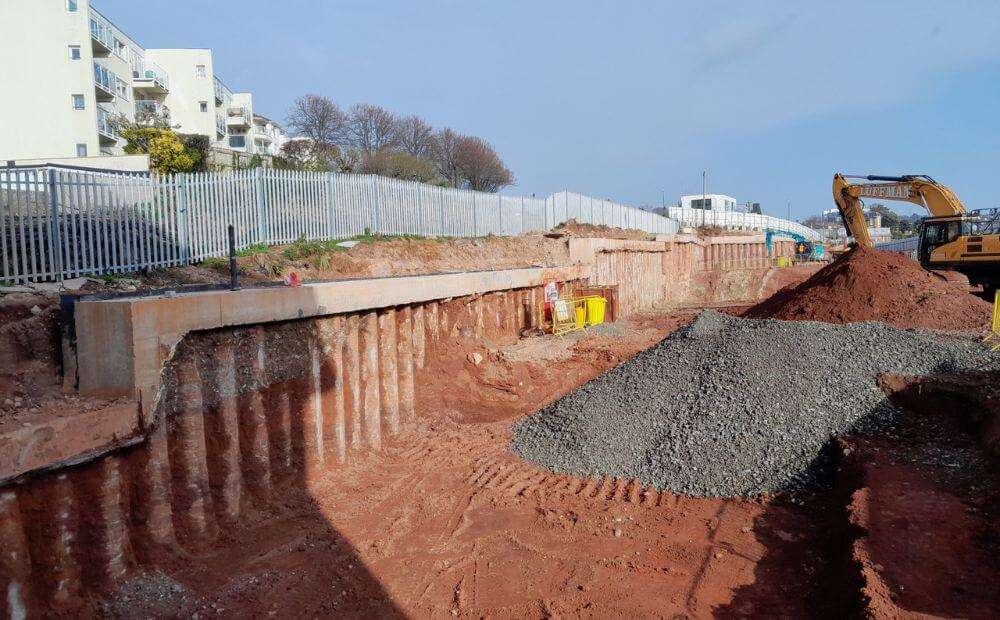
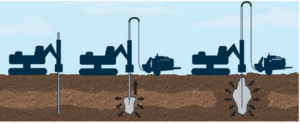
Contiguous pile walls consist of vertical piles driven or drilled into the ground, spaced closely together to form a continuous barrier. Unlike other pile wall systems such as secant or tangent piles, contiguous pile walls feature piles that are placed adjacent to each other, but without overlapping. The gaps between the piles are typically small—often between 3 to 6 inches—creating a wall that serves as an effective earth retention system.
These walls are primarily used for excavation support in areas where deep digging is necessary, such as for basements, tunnels, or underground parking structures.
Applications of Contiguous Pile Walls
Contiguous pile walls are versatile and can be applied to a variety of construction projects. Some of the most common applications include:
1. Basements and Underground Structures
- Deep Excavations: Ideal for projects requiring excavation below the water table or in areas with weak surface soils.
- Retaining Walls for Underground Parking: Prevent soil movement and provide the structural integrity needed for large, underground spaces.
2. Waterfront Construction
Seawalls and Docks: Provide stability and control water ingress in coastal and riverfront developments.
Flood Protection: Used in flood-prone areas to help prevent water penetration into the excavation site.
3. Cut-and-Cover Tunnels
- Excavation Support: Used to provide a stable boundary during the construction of underground tunnels, such as those for subway systems.
- Retaining Earth: Helps to keep the surrounding soil from collapsing while tunnel construction is underway.
4. Slope Stabilization
- Preventing Landslides: In mountainous regions or sloped terrains, contiguous pile walls help stabilize the earth and prevent shifting or landslides.
Advantages of Contiguous Pile Walls
Contiguous pile walls offer several key benefits that make them an attractive solution for deep excavation projects:
1. Effective Earth Retention
Contiguous pile walls are highly effective in supporting deep excavations, preventing soil movement, and controlling groundwater infiltration. The closely spaced piles form a solid barrier that resists lateral soil pressure, ensuring the stability of the excavation site.
2. Minimal Ground Disturbance
Installation of contiguous pile walls creates minimal vibration and noise compared to other piling methods, which is particularly advantageous in urban areas where surrounding structures must be protected from damage.
3. Cost-Effective
When compared to more complex pile wall systems like secant piles, contiguous pile walls can be a more economical solution for many projects. The construction process is faster and requires less material due to the absence of overlapping piles.
4. Flexibility in Design
Contiguous pile walls can be adapted to different depths, pile sizes, and spacing to suit the specific needs of a project. The system is versatile enough to handle varying load conditions and soil types.
5. Space Efficiency
Since the piles are closely spaced, contiguous pile walls take up less space on the site, making them ideal for projects with limited available land or for applications where maintaining existing structures and infrastructure is essential.
Installation Process for Contiguous Pile Walls
The installation of contiguous pile walls typically follows these general steps:
1. Site Preparation:
The area is cleared, and excavation to the required depth begins, ensuring that the site is ready for pile installation.
2. Pile Installation:
Piles are drilled or driven into the ground along the predetermined alignment. The spacing between each pile is kept consistent to create the continuous barrier.
3. Grouting and Reinforcement:
Once the piles are in place, grout is injected to enhance the bonding between the piles and the surrounding soil. Steel reinforcement may be added for additional strength, depending on the load-bearing requirements.
4. Cutting and Leveling:
The tops of the piles are cut to a uniform level, ensuring the wall’s overall structural integrity.
5. Backfilling and Finishing:
Any remaining excavation is backfilled, and finishing work, such as the installation of drainage systems or waterproofing membranes, may be carried out if necessary.
Challenges and Considerations
While contiguous pile walls offer numerous advantages, there are some challenges to consider:
1. Waterproofing
Since contiguous pile walls do not overlap, they may not be fully watertight. In applications where water penetration is a concern, additional waterproofing measures or membrane installations may be necessary.
2. Space Constraints
The installation of contiguous pile walls requires sufficient space for pile driving or drilling equipment. In densely built environments, access to the site can sometimes be a limiting factor.
4. Soil Conditions
The effectiveness of contiguous pile walls depends on the soil conditions. In loose or highly saturated soils, additional measures may be needed to ensure the stability and performance of the wall.
5. Cost Considerations
While cost-effective in many situations, the cost of contiguous pile walls can vary depending on the soil conditions, depth, and complexity of the project. It is important to evaluate the project requirements and compare alternative solutions.
Conclusion
Contiguous pile walls are a proven and efficient solution for managing deep excavations, providing earth retention and groundwater control in challenging soil conditions. Whether supporting the construction of basements, tunnels, or waterfront structures, these walls offer substantial benefits, including flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and minimal disturbance to the surrounding environment.