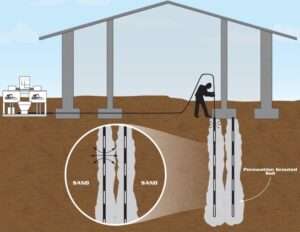
Rock fissure grouting is an advanced technique used in geotechnical engineering to enhance the stability and strength of rock formations by filling fractures, voids, and fissures with specialized grout materials. This method plays a crucial role in improving the structural integrity of foundations, reducing water ingress, and preventing potential hazards in various construction projects. Understanding the process and benefits of rock fissure grouting is key to its successful application in ground improvement.
What is Rock Fissure Grouting?
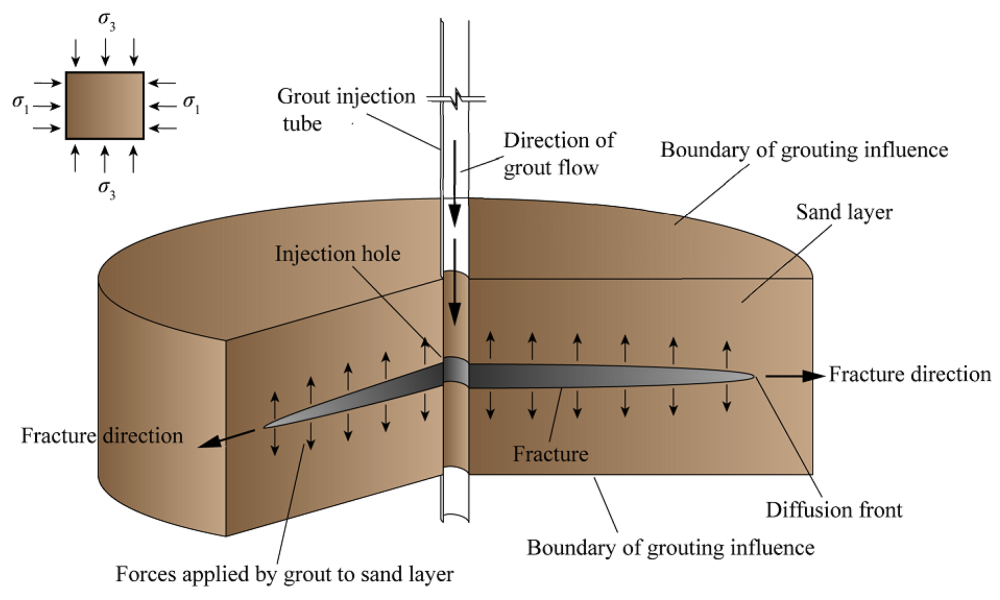
Rock fissure grouting involves injecting a grout mixture into natural fractures, cracks, and voids within rock masses. The purpose is to fill these voids and bind fractured rock together, which improves its overall strength, reduces permeability, and stabilizes the formation. This process is particularly useful in situations where traditional methods of ground improvement are ineffective or too costly.
The grout used in fissure grouting typically consists of cement-based materials, chemical grout, or polymer resins. These materials are injected through a series of drilled boreholes at precise locations within the rock formation. As the grout flows into the fissures, it hardens and creates a more cohesive structure, effectively reducing the risk of ground instability, water leakage, or erosion.
The Process of Rock Fissure Grouting
1.Site Investigation and Pre-Drilling
The first step in rock fissure grouting is a thorough site investigation, which includes geotechnical surveys to identify the locations, size, and extent of fissures in the rock. Boreholes are then drilled into these identified areas to allow for precise grout injection.
2.Grout Selection and Preparation
Once the fissures are located, the appropriate grout mix is selected based on the type of rock, the size of the fissures, and the project’s specific requirements. The grout is then mixed and prepared for injection.
3.Injection of Grout
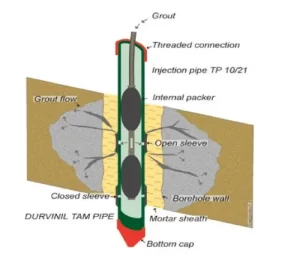
The grout is injected into the rock fissures through the boreholes. The injection is carefully controlled to ensure that the grout fills the fissures and fractures effectively. Multiple injections may be required to fully seal larger or more complex fissures.
4.Curing and Monitoring
After the grout has been injected, it is allowed to cure and harden within the fractures. The grouting process is monitored to ensure that the grout penetrates effectively and that the desired improvements are achieved. Additional injections may be made if necessary.
5.Post-Application Evaluation
Once the grouting process is complete, follow-up inspections and tests are conducted to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. This may include checking for improvements in rock strength, reduced permeability, and the overall stability of the formation.
Benefits of Rock Fissure Grouting
1.Increased Structural Stability
By filling fissures and fractures, rock fissure grouting significantly increases the load-bearing capacity of the rock. This makes the underlying foundation more stable and capable of supporting larger and heavier structures.
2.Reduced Water Infiltration
Fissures in rock formations can act as pathways for groundwater, leading to erosion, soil movement, or even water seepage into tunnels and foundations. Rock fissure grouting reduces permeability, effectively sealing off these water paths and preventing further seepage.
3.Enhanced Durability and Longevity
Grouting strengthens the rock by binding fractured sections together, increasing the durability and longevity of the rock formation. This is especially important for infrastructure projects such as dams, bridges, and tunnels, which must withstand long-term stresses and environmental conditions.
4.Cost-Effectiveness
Rock fissure grouting is often more cost-effective than alternative methods of ground improvement, such as excavation or full-scale rock removal. It offers a targeted solution to address specific weaknesses without requiring large-scale interventions, which can be more expensive and time-consuming.
5.Prevention of Sinkholes and Ground Instability
In areas where rock fissures are prevalent, the risk of sinkholes or sudden ground collapse can pose significant threats to both safety and infrastructure. By stabilizing these fractures, rock fissure grouting reduces the likelihood of such occurrences, improving the safety of the site.
6.Minimal Disruption
Compared to other ground improvement methods, rock fissure grouting is minimally invasive. It does not require large excavation works or disruption to the surrounding environment, making it suitable for projects in sensitive or urban areas.
Applications of Rock Fissure Grouting
Rock fissure grouting is widely used in various geotechnical applications, such as:
- Tunnel Construction: Sealing fissures in rock formations to prevent water ingress and ensure the stability of underground tunnels.
- Dam Construction: Strengthening rock foundations beneath dams to support their weight and prevent erosion or seepage.
- Bridge and Highway Foundations: Enhancing the stability of rock formations that serve as the foundation for bridge piers, roadways, and embankments.
- Mining Operations: Stabilizing rock in open-pit or underground mines to prevent collapse and improve safety.
- Slope Stabilization: Reducing the risk of landslides in areas with fractured rock or loose soil.
Conclusion
Rock fissure grouting is an essential technique in geotechnical engineering for enhancing the stability, strength, and durability of rock foundations. By addressing the challenges posed by fissures and fractures, this method helps ensure the safety and longevity of infrastructure projects. With its ability to reduce water infiltration, prevent ground instability, and provide a cost-effective solution to complex problems, rock fissure grouting continues to be a valuable tool in ground improvement across a wide range of applications.