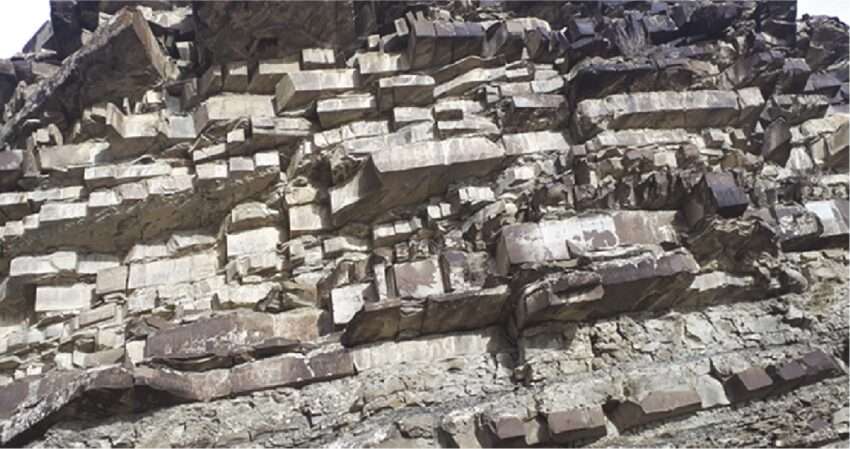
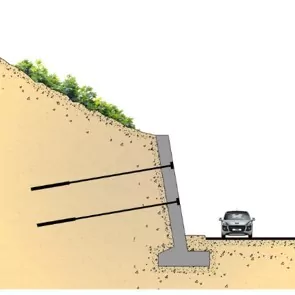
Rock fissure grouting is an essential technique used to stabilize and reinforce rock masses, ensuring their safety and reliability in construction projects. This method is commonly employed in situations where natural or induced fractures, cracks, or voids within rock formations compromise the structural integrity of the ground. By injecting specialized grout into these fissures, engineers can enhance the strength, permeability, and overall stability of the rock, making it suitable for a variety of construction applications, including tunnels, dams, foundations, and slopes.
What is Rock Fissure Grouting?
Rock fissure grouting is the process of injecting grout—typically a mixture of cement, water, and chemical additives—into fractures, fissures, or voids within rock masses. The goal is to fill the cracks, bind fragmented rock particles, and reduce the permeability of the rock, thereby improving its load-bearing capacity and preventing water infiltration.
Grouting helps stabilize rock masses that are otherwise too fractured or porous to support large-scale construction projects. It also helps control groundwater flow, making it especially valuable in tunnel construction, dam engineering, and other underground structures.
Techniques Used in Rock Fissure Grouting
Several techniques are employed in rock fissure grouting, each suited for different rock types and project conditions. These methods include:
1.Permeation Grouting
-
- Involves injecting grout into the rock mass to permeate the fissures without displacing the surrounding rock.
- Used when the fractures are small or narrow, and the goal is to reduce permeability and improve the rock’s structural integrity.
2.Fracture Grouting
-
- High-pressure grout injection creates fractures within the rock mass, allowing the grout to penetrate and fill larger voids and cracks.
- This method is effective in highly fractured rock masses where larger voids need to be sealed.
3.Compaction Grouting
-
- A more rigid grout mixture is injected under high pressure to compact and stabilize loose or fragmented rock layers.
- Ideal for situations where there is significant void space or weak, fractured rock layers that need to be densified.
4.Jet Grouting
-
- This technique involves injecting a high-pressure jet of grout into the rock, breaking up the rock structure and mixing it with the grout to form a solidified mass.
- Jet grouting is particularly effective for creating solid columns of reinforced rock, improving the overall mass stability.
Key Benefits of Rock Fissure Grouting
1.Increased Rock Stability
-
- Grouting helps to bind fractured rock masses, preventing further rock movement and improving overall structural integrity. This is crucial for ensuring the stability of buildings, tunnels, and other structures built on or within rock formations.
2.Waterproofing
-
- Rock fissure grouting reduces the permeability of the rock mass, preventing water seepage through cracks. This is particularly important in underground construction, such as tunnels and foundations, where water ingress can weaken structures and create hazardous conditions.
3.Cost-Effective Solution
-
- Compared to other ground improvement methods, grouting is often more affordable and faster, making it a popular choice in both large-scale infrastructure projects and smaller-scale applications.
4.Prevents Settlement
-
- By reinforcing and stabilizing fractured rock, grouting reduces the risk of uneven settlement under structures, preventing foundation issues that could arise from unstable ground.
5.Minimized Surface Disruption
-
- As an injection technique, rock fissure grouting requires minimal surface disturbance, making it suitable for projects in urban areas or other sensitive environments where excavation or surface disruption would be impractical.
Applications of Rock Fissure Grouting
1.Tunnel and Underground Construction
-
- Rock fissure grouting is frequently used in tunnel construction to stabilize surrounding rock and control groundwater flow, ensuring a dry and secure working environment for tunnel workers.
2.Dam Engineering
-
- Grouting is critical in dam construction, where it is used to seal fractures in the foundation rock and prevent seepage, ensuring the dam’s stability and integrity.
3.Slope Stabilization
-
- In areas prone to landslides or rockfalls, rock fissure grouting can stabilize fractured rock faces, reducing the risk of rock movement and improving slope stability.
4.Foundation Support
-
- When a foundation is being constructed on rock with large fissures or voids, grouting can be used to fill the gaps, stabilize the rock, and provide a solid base for the foundation.
5.Mining Operations
-
- In underground mining, grouting can be used to stabilize the rock mass and prevent dangerous collapses or flooding caused by groundwater infiltration.
Challenges in Rock Fissure Grouting
1.Grout Penetration
-
- In some cases, the grout may not adequately penetrate highly fractured or impermeable rock formations. This can limit the effectiveness of the grouting process, requiring additional measures or techniques to ensure proper grout distribution.
2.Grout Selection
-
- The choice of grout material is crucial to the success of the process. Factors such as rock type, fracture size, and groundwater conditions must be considered to select the right mixture of cement, chemical additives, and other materials.
3.Pressure Control
-
- The injection of grout at excessively high pressure can cause unintended fractures or damage to the surrounding rock mass, requiring careful monitoring and control of the grouting process.
4.Environmental Impact
-
- While rock fissure grouting is generally considered a safe method, the injection of chemicals and grout materials can have environmental impacts, particularly if there is poor control over grout leakage or contamination of groundwater.
Conclusion
Rock fissure grouting is an indispensable technique for reinforcing and stabilizing rock masses in construction projects. By effectively filling fractures and reducing permeability, this method ensures the safety and stability of structures built on or within rock formations. Whether used in tunneling, dam construction, or slope stabilization, rock fissure grouting continues to play a vital role in modern geotechnical engineering, providing a reliable and cost-effective solution for challenging ground conditions.
This article highlights the significance of rock fissure grouting, its methods, benefits, and applications in ensuring the safety and stability of construction projects built in or around fractured rock formations.