Tam grouting, also known as tube-à-manchette grouting, is a specialized technique in geotechnical engineering used to improve soil properties, enhance structural stability, and control water flow in challenging ground conditions. This method is particularly valuable for its precision and ability to target specific subsurface zones, making it an indispensable tool for engineers working in complex geotechnical scenarios.
What is Tam Grouting?
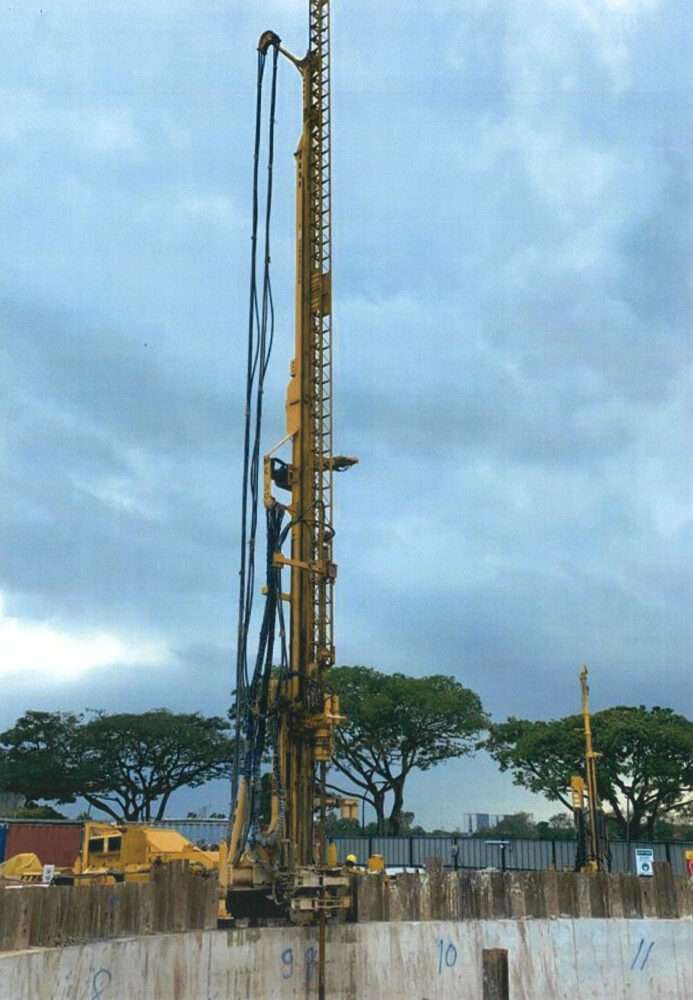
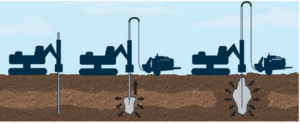
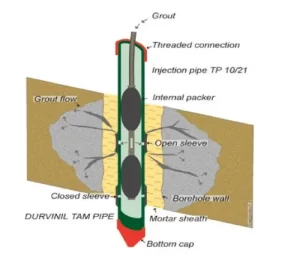
Tam grouting involves the use of a tube-à-manchette, a perforated pipe with rubber sleeves covering its holes, which is inserted into a pre-drilled borehole. Grout—a mixture of cement, water, or other binding materials—is injected under pressure through these sleeves to improve the ground’s strength, fill voids, or reduce permeability. The sleeves act as one-way valves, allowing grout to flow into the soil while preventing backflow into the pipe. This controlled and repeatable injection process distinguishes tam grouting from other methods.
Key Applications of Tam Grouting
Tam grouting is employed in a variety of geotechnical engineering contexts, including:
1.Foundation Stabilization
This method is used to strengthen soil beneath foundations, ensuring even load distribution and preventing settlement or tilting in structures.
2.Groundwater Control
In tunneling and excavation projects, tam grouting creates impermeable barriers that prevent water ingress, protecting both the site and surrounding structures.
3.Void Filling
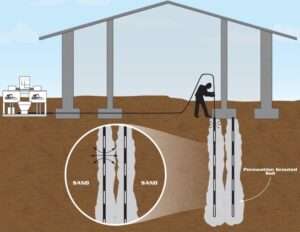
It effectively fills subsurface voids in karst terrain or under existing infrastructure, preventing sudden collapses or sinkhole formation.
4.Soil Reinforcement for Deep Excavations
By increasing soil cohesion, tam grouting stabilizes deep excavations, making it safer to construct basements, subways, or other below-grade facilities.
5.Slope and Embankment Stability
It enhances the integrity of slopes and embankments, reducing the risk of landslides and erosion, especially in seismically active areas.
Benefits of Tam Grouting
1.Precision and Targeted Application
Tam grouting allows for the selective improvement of specific subsurface zones without disturbing adjacent areas, making it ideal for sensitive projects near existing structures.
2.Enhanced Soil Strength and Durability
The injected grout increases the soil’s load-bearing capacity, reduces its deformability, and provides long-term stability.
3.Cost-Effective Solution
By addressing localized weak spots rather than replacing entire soil strata, tam grouting offers a cost-efficient alternative to more invasive ground improvement methods.
4.Reduced Permeability
The technique creates watertight barriers, minimizing risks of flooding, erosion, and contamination in projects requiring groundwater management.
5.Versatility
Tam grouting is compatible with various soil types, including loose sands, silts, and fractured rock, allowing it to be used in diverse geotechnical applications.
Challenges and Considerations
While tam grouting offers significant benefits, its success depends on thorough site investigation, precise execution, and monitoring. Poorly executed grouting can lead to over-pressurization, causing ground heave or damage to adjacent structures. Additionally, selecting the appropriate grout mix and injection parameters is critical to achieving the desired results.
Conclusion
Tam grouting is a powerful technique that combines precision and versatility to address geotechnical challenges in modern construction. From stabilizing foundations to managing groundwater, its applications span a wide range of engineering needs. By enhancing soil properties and ensuring the safety and durability of structures, tam grouting continues to play a pivotal role in shaping resilient infrastructure for the future.