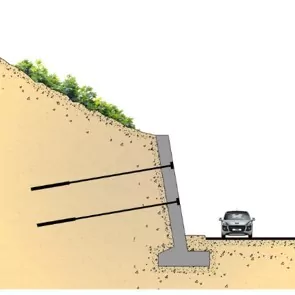
In the world of geotechnical engineering, the stability and safety of a structure often depend on its foundation system. Micro piles, also known as mini piles, are a versatile and increasingly popular foundation solution used to address challenging soil conditions and site constraints. With their ability to bear substantial loads despite their small diameter, micro piles are revolutionizing construction practices across various industries.
What Are Micro Piles?
Micro piles are slender, high-capacity, deep foundation elements that typically range from 150 mm to 300 mm in diameter. They consist of a steel casing or reinforcement bar (rebar) encased in cement grout. Despite their small size, micro piles can carry heavy loads due to their innovative design and the efficient transfer of loads to deeper, stable soil layers.
Key Features:
- Diameter: Smaller than traditional piles, typically less than 300 mm.
- Installation Depth: Can extend to depths exceeding 30 meters, depending on the project requirements.
- Load Capacity: Capable of supporting axial loads of up to 500 tons or more.
Applications of Micro Piles
Micro piles are highly adaptable, making them suitable for a wide range of geotechnical applications:
1. Foundation Support
Micro piles are often used to strengthen or replace existing foundations, particularly in urban environments where space is limited and vibration must be minimized.
2. Slope Stabilization
In landslide-prone areas, micro piles are deployed to stabilize slopes and prevent soil erosion by reinforcing weak ground.
3. Seismic Retrofitting
In regions with high seismic activity, micro piles enhance the resilience of existing structures by providing additional support and damping capacity.
4. Underground Construction
Micro piles are essential in tunneling and mining projects, where they act as ground anchors or temporary supports to stabilize excavations.
5. Load Transfer in Weak Soils
Micro piles transfer structural loads to deeper, more stable strata, bypassing weak or compressible surface layers.
Advantages of Micro Piles
Micro piles offer numerous benefits that make them a preferred choice for challenging geotechnical conditions:
1. Adaptability to Difficult Conditions
Micro piles can be installed in tight spaces, beneath existing structures, and in environments with restricted access. They are ideal for sites with poor soil quality, high groundwater levels, or obstructions like boulders.
2. Minimal Disturbance
The installation process generates low noise and vibration, making micro piles suitable for urban and environmentally sensitive areas.
3. High Load-Bearing Capacity
Despite their small size, micro piles can support significant loads, both in tension and compression. This strength makes them suitable for high-rise buildings, bridges, and other heavy structures.
4. Quick Installation
Modern drilling techniques allow for rapid installation, reducing project timelines and minimizing disruptions.
5. Seismic Resistance
Micro piles improve the seismic performance of structures by absorbing and redistributing seismic forces.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial cost of micro piles may be higher than some alternatives, their adaptability and minimal site preparation can result in overall savings.
Installation Process
The installation of micro piles involves several precise steps:
1. Site Preparation: Engineers evaluate soil conditions and design the micro pile configuration.
2. Drilling: A small-diameter borehole is drilled to the required depth using specialized equipment.
3. Reinforcement Placement: A steel rebar or casing is inserted into the borehole.
4. Grouting: High-strength cement grout is injected to fill the borehole and bond the pile with the surrounding soil or rock.
5. Load Testing: The completed micro piles are tested to ensure they meet the required load-bearing capacity.
Innovations in Micro Pile Technology
Advances in materials and construction techniques continue to enhance the performance of micro piles:
- Self-Drilling Micro Piles: Combine drilling and grouting into a single process, speeding up installation.
- Fiber-Reinforced Grout: Improves the durability and load-bearing capacity of the grout material.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors embedded in micro piles provide real-time data on load and displacement, ensuring long-term performance.
Case Studies
1. Retrofit of Historic Structures
Micro piles have been used to reinforce aging buildings in urban areas without disturbing their architectural integrity. For instance, they were integral in preserving Venice’s historic foundations.
2. Bridge Support in Challenging Terrain
In mountainous regions, micro piles have successfully stabilized bridge abutments and piers on slopes with weak soils and high seismic risks.
3. Post-Disaster Reconstruction
Following earthquakes or landslides, micro piles are deployed to stabilize damaged foundations and enable rapid rebuilding.
Conclusion
Micro piles are a cornerstone of modern geotechnical engineering, offering unmatched versatility and strength in challenging conditions. Their ability to support heavy loads, adapt to constrained sites, and minimize environmental impact makes them indispensable in contemporary construction projects.