Shotcrete has become an indispensable tool in the arsenal of civil engineers, offering a powerful solution for protecting and stabilizing slopes and tunnels. This article will delve into the world of shotcrete, exploring its applications, techniques, and benefits in the realm of civil engineering.
The Basics of Shotcrete
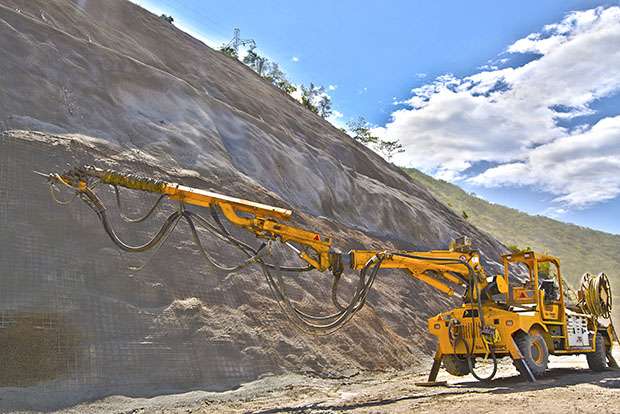
Shotcrete is a type of concrete that’s pneumatically applied at high velocity onto a surface. This process involves mixing cement, aggregate, and water, then spraying the mixture through a hose using compressed air. The result is a dense, durable layer of concrete that adheres tightly to the substrate.
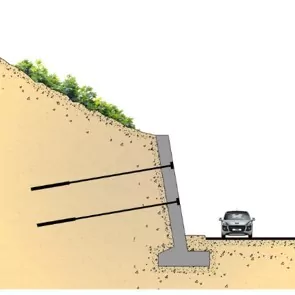
Shotcrete in Slope Protection
Shotcrete plays a critical role in protecting and stabilizing slopes, particularly in areas prone to erosion, landslides, and rockfalls. The process of applying shotcrete to a slope typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The slope is cleaned and prepared to ensure a strong bond between the shotcrete and the substrate.
- Application: The shotcrete mixture is pneumatically applied to the slope, building up a layer of the desired thickness.
- Reinforcement: If required, reinforcing mesh or fibers are embedded into the wet shotcrete to add additional strength.
- Finishing: The shotcrete is finished to the desired texture and appearance.
Shotcrete acts as both a protective coating, shielding the slope from weathering and erosion, and a structural reinforcement, helping to prevent slope failures. Its high strength, strong adhesion, and ability to be applied to complex geometries make it an ideal solution for slope protection.
Shotcrete in Tunnel Protection
Shotcrete is also widely used in tunnel construction and rehabilitation, serving as a primary lining that provides immediate support and stabilization. The process of shotcrete application in tunnels involves:
- Preparation: The tunnel substrate is cleaned and prepared to ensure a strong bond with the shotcrete.
- Application: The shotcrete mixture is pneumatically applied to the tunnel surface, building up a layer of the desired thickness.
- Reinforcement: Reinforcing mesh or fibers are typically embedded into the wet shotcrete to add additional strength.
- Finishing: The shotcrete is finished to the desired texture and appearance.
Shotcrete helps to prevent rockfalls and tunnel collapse, provides a durable layer of protection against water ingress and corrosion, and can even improve the fire resistance of the tunnel.
Techniques and Considerations
Several techniques and considerations come into play when working with shotcrete in civil engineering applications:
- Mix Design: The shotcrete mix must be carefully designed to achieve the desired properties, such as high strength, low rebound, and good pumpability.
- Application Technique: The nozzleman’s skill and technique play a critical role in achieving a high-quality shotcrete layer.
- Reinforcement: The type and amount of reinforcement used will depend on the specific requirements of the project.
- Curing: Proper curing is essential to ensure the shotcrete achieves its full potential properties.
- Quality Control: Regular testing and inspection are necessary to ensure the shotcrete meets the project specifications.
Innovations in Shotcrete Technology
The world of shotcrete is continually evolving, with new innovations and advancements improving its performance and applicability. These include:
- Fiber Reinforcement: The use of synthetic and steel fibers is becoming increasingly popular, offering improved tensile strength and durability.
- Specialized Mix Designs: New mix designs are being developed to improve shotcrete’s resistance to sulfates, acids, and other forms of degradation.
- Spraying Technologies: Advances in spraying equipment are allowing for greater control over the application process, improving quality and efficiency.
- Additives: New additives are being developed to improve shotcrete’s workability, pumpability, and finishing characteristics.
Case Studies
Shotcrete has been used in countless civil engineering projects around the world. A few notable examples include:
- The Gotthard Base Tunnel: Shotcrete was used as the primary lining for this 57km long railway tunnel through the Swiss Alps.
- The Second Avenue Subway: Shotcrete was used to stabilize the tunnel and station caverns for this major expansion of the New York City subway system.
- The California High-Speed Rail: Shotcrete is being used to stabilize slopes and protect tunnels along the route of this high-speed rail project.
Conclusion
Shotcrete has proven itself as a highly effective technique for protecting and stabilizing slopes and tunnels in civil engineering. Its unique combination of high strength, strong adhesion, and rapid application make it a go-to solution for engineers and contractors. As the demands of infrastructure projects continue to grow and the challenges of climate change intensify, the role of shotcrete in safeguarding our built environment will only become more crucial. By embracing new innovations and best practices, we can unlock the full potential of shotcrete and build a more resilient future.